I created this tutorial as I could not find a simple and easy to integrate a CMS with a static site generator (SSG).
All the SSGs have a single issue that you have to edit the markdown directly. You need to have the project set up on your device. There is no admin interface to easily edit the content of the website. The tutorials available are not easy to understand and implement. But in this tutorial I’ll also show you how to add DecapCMS to an existing Astro project to edit the site using an admin interface.
Getting started#
For this tutorial we’ll need the following:
- Node.js (v22+).
- A Github and Vercel account (its free).
- A project in which you want to add DecapCMS. We’ll use the Astro blog template for this tutorial.
- A custom domain (not mandatory but good to have).
Setting up the Astro site#
Cloning the starter project#
Create a new project with the Astro blog template. You can keep the directory name as blog.
npm create astro@latest -- --template blog
After following the steps you’ll have the following directory structure.
📦blog
┣ 📂.vscode
┣ 📂public
┣ 📂src
┣ 📜.gitignore
┣ 📜README.md
┣ 📜astro.config.mjs
┣ 📜package-lock.json
┣ 📜package.json
┗ 📜tsconfig.json
Now, run the project.
npm dev
And go to http://localhost:4321. You’ll be able to see the site.
Adding a post#
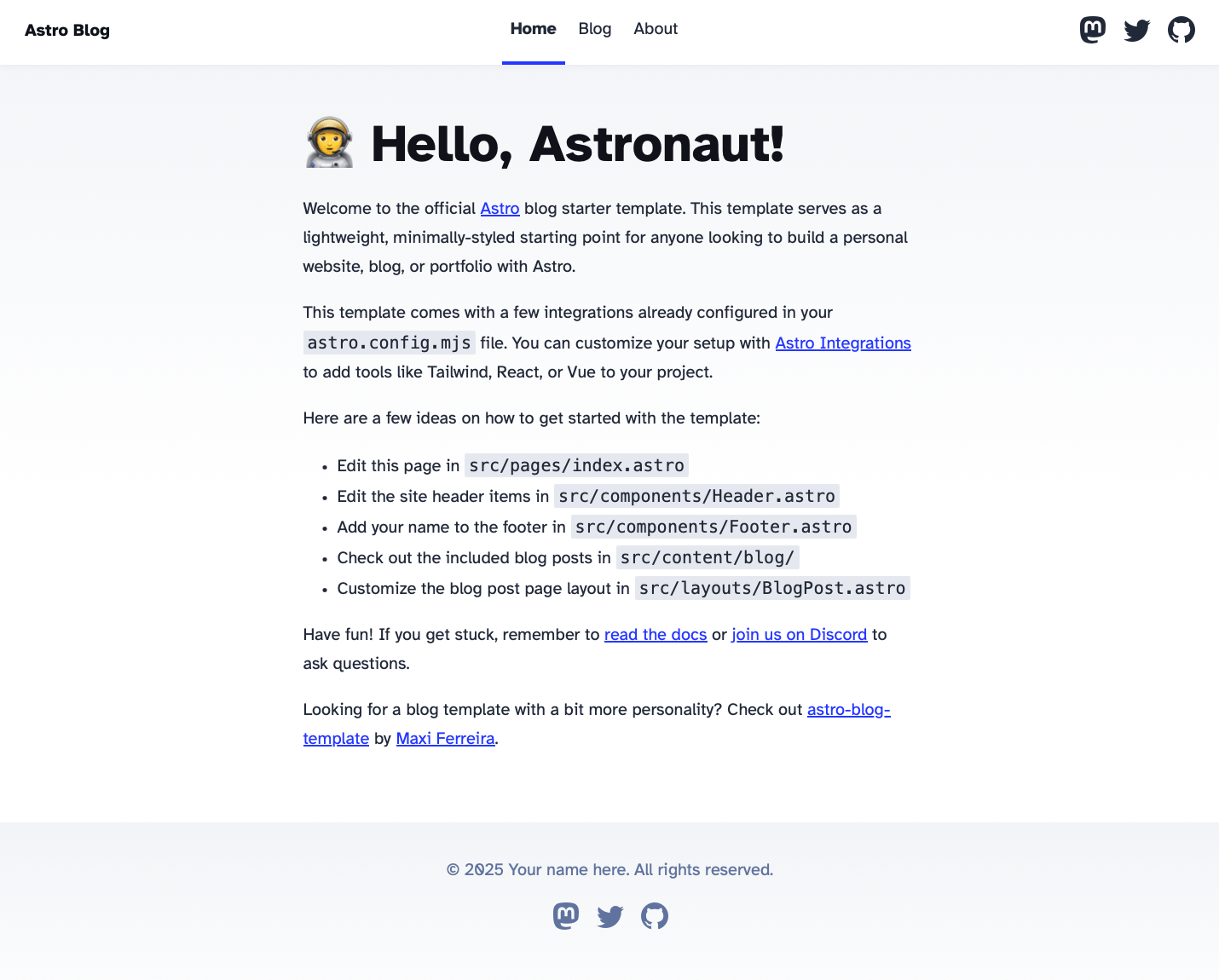
Now we’ll add a post to the site. Go to src/content/blog and create a file named test.md
---
title: "Test 1"
description: "created using code editor"
pubDate: "Mar 27 2025"
heroImage: "/blog-placeholder-4.jpg"
---
This is a test post
Save the file and go to the blog section of the site. Open the Test 1 post.
Deploying the site#
Your site is now ready to be deployed. First we’ll push the code to Github and then deploy it using vercel.
Pushing to Github#
Create an empty repository in Github and push the code.
git remote add origin <your repository url>
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
Deploy on vercel#
Login to Vercel using Github for easy configuration. Then add a new project. Choose Import Git Repository.
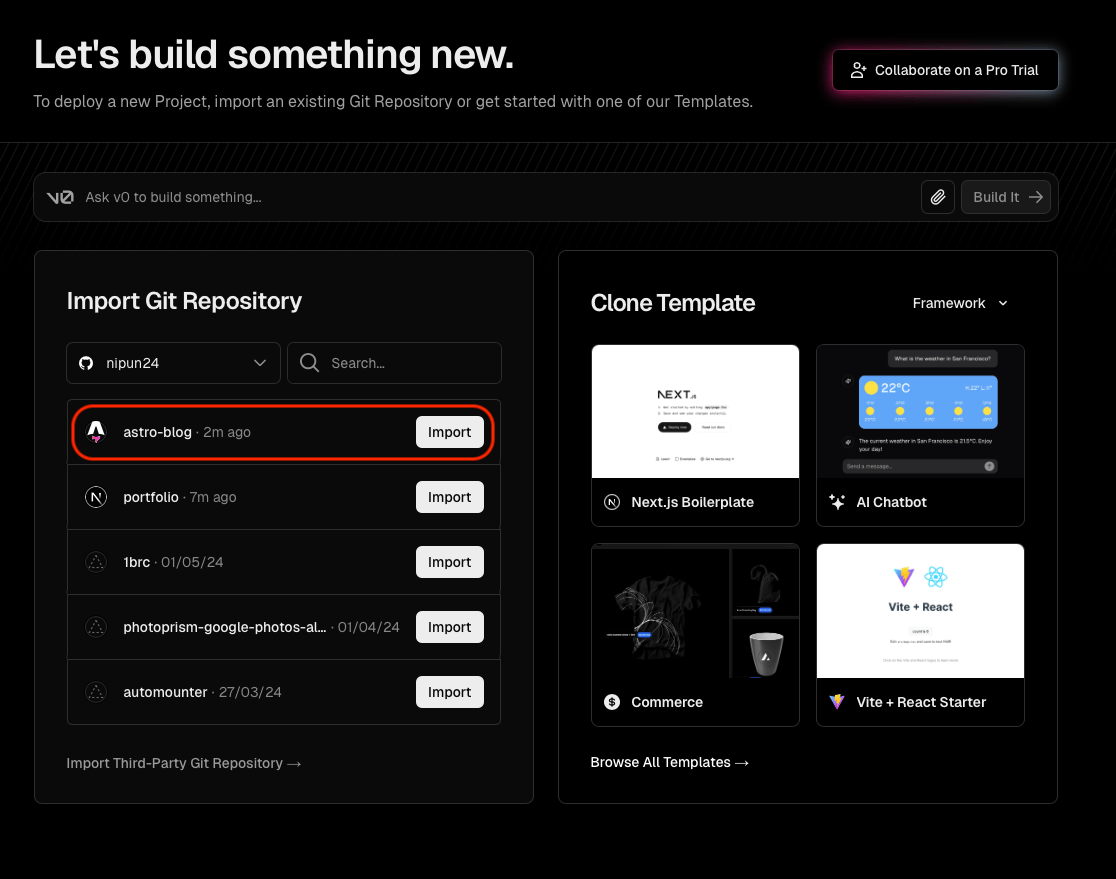
Finally, click Deploy.
Wait for the site to get deployed. When the site is deployed click on the url to open the site.
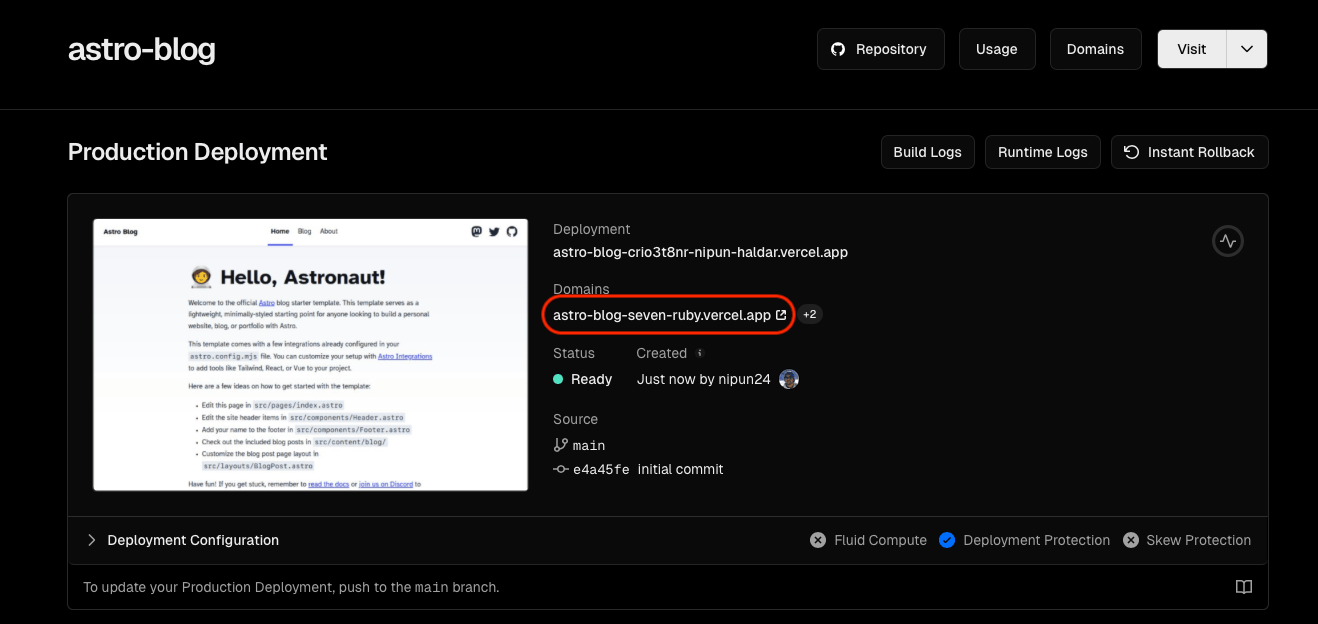
Now if you add a post and push to your repository, vercel will automatically build and deploy the site. But this becomes clunky if you do not have access to you machine with the repository setup locally. So to make it easier to add and edit posts well add DecapCMS so that you can edit the blog from anywhere through an interface in your browser only.
Adding DecapCMS#
Configuring DecapCMS#
Create two files inside public/admin/
📦public
┣ 📂admin
┃ ┣ 📜config.yml
┃ ┗ 📜index.html
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta name="robots" content="noindex" />
<link href="/admin/config.yml" type="text/yaml" rel="cms-config-url" />
<title>Content Manager</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Include the script that builds the page and powers Decap CMS -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/decap-cms@^3.0.0/dist/decap-cms.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
config.yml
collections:
- name: "blog" # Used in routes, e.g., /admin/collections/blog
label: "Blog" # Used in the UI
folder: "src/content/blog" # The path to the folder where the documents are stored
create: true # Allow users to create new documents in this collection
fields: # The fields for each document, usually in frontmatter
- { label: "Title", name: "title", widget: "string" }
- { label: "Description", name: "description", widget: "string" }
- { label: "Publist date", name: "pubDate", widget: "datetime" }
- { label: "Hero image", name: "heroImage", widget: "string" }
media_folder: "src/assets/images" # Location where files will be stored in the repo
public_folder: "src/assets/images" # The src attribute for uploaded media
backend:
name: github
repo: <owner-name>/<repo-name>
branch: main
Now open http://localhost:4321/admin/index.html and click Login with GitHub.

If everything worked you will be able to see all your posts.
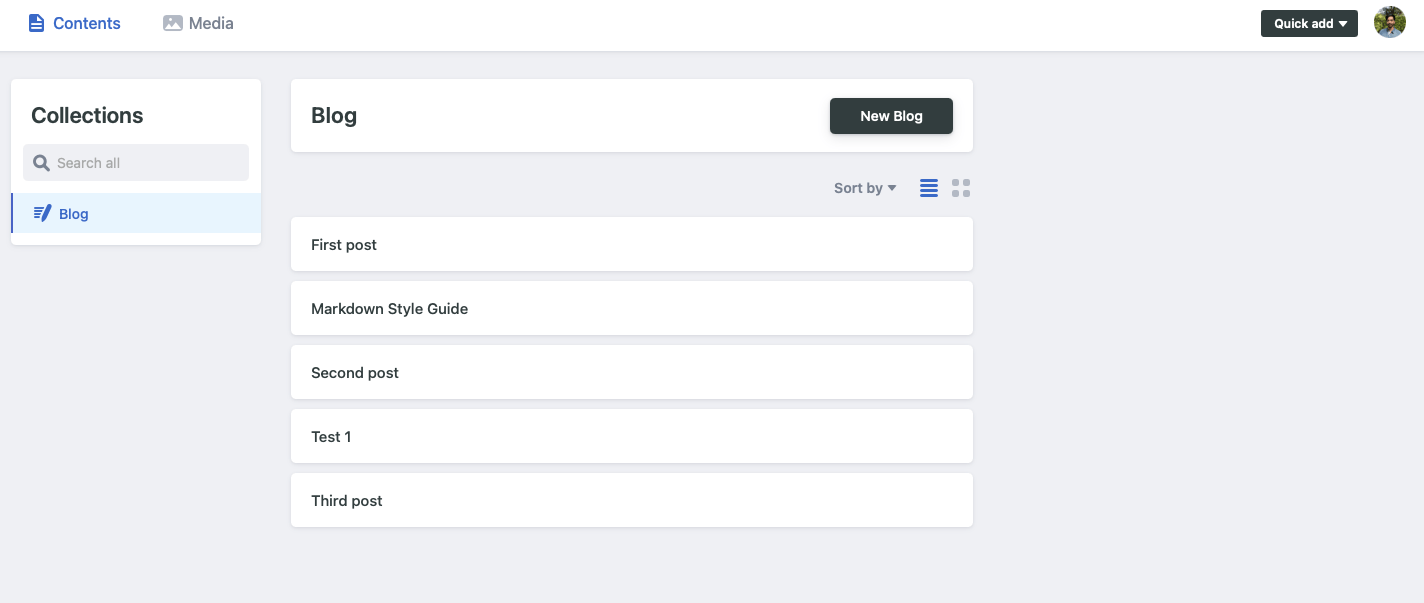
Editing a post#
Open the post we just created and edit it. When you are done click on Publish. DecapCMS will push a commit with the changes to your Github repository and vercel will start the build. Wait for the build to finish and see the changes.
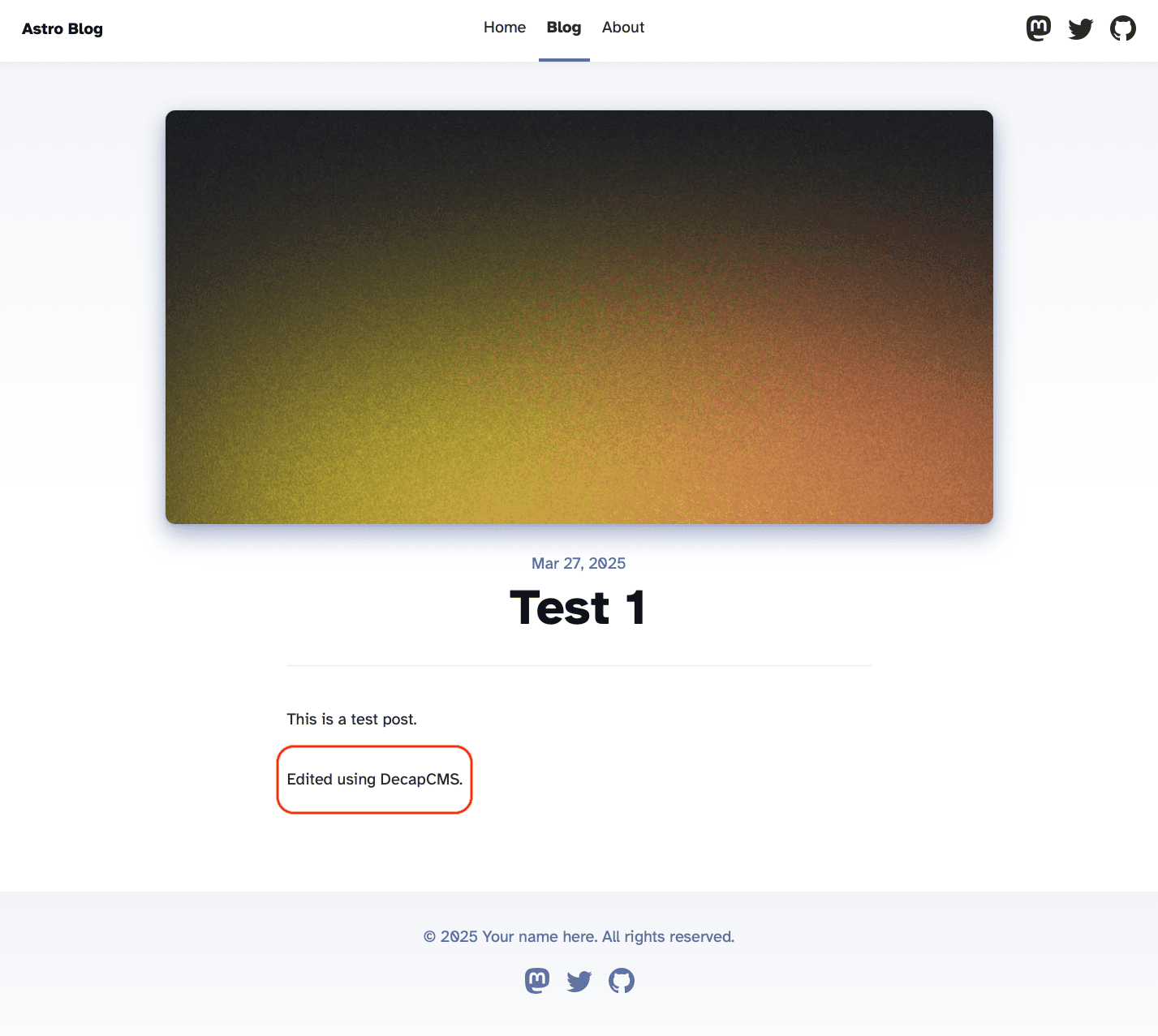
You’ll not be able to edit the posts just yet from the public url on vercel. Commit and push all your changes to Github. We’ll need to configure the OAuth for production use.
Creating OAuth for production#
Create Github OAuth application#
Login to Github and go to Profile > Developer Settings > OAuth Apps > New OAuth app.
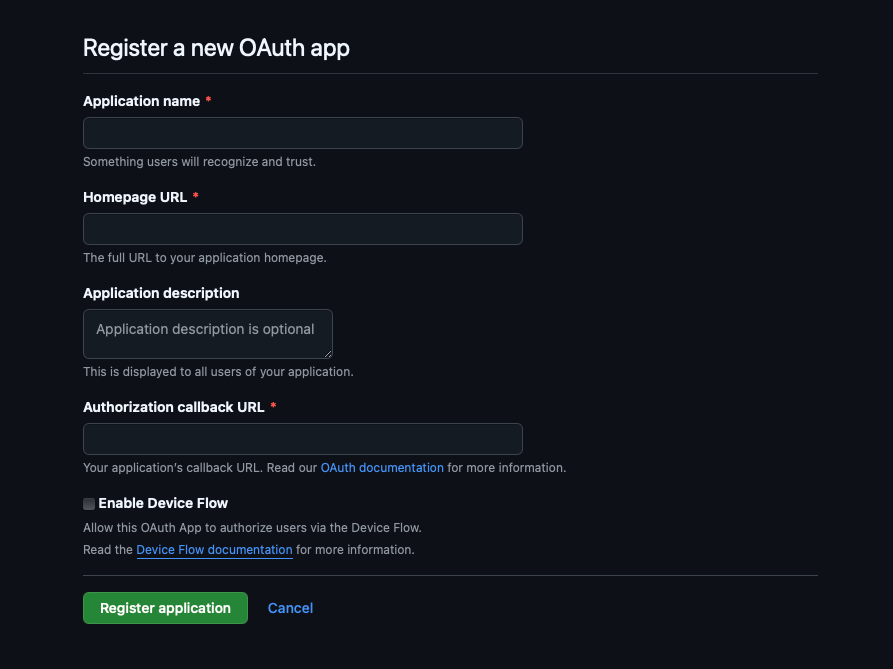
Enter the following values:
- Application name: blog (can be anything)
- Homepage URL: vercel public url of the app
- Application Description: decap oauth (can be anything)
- Authorization callback URL:
/api/callback - Enable Device Flow: Keep unchecked
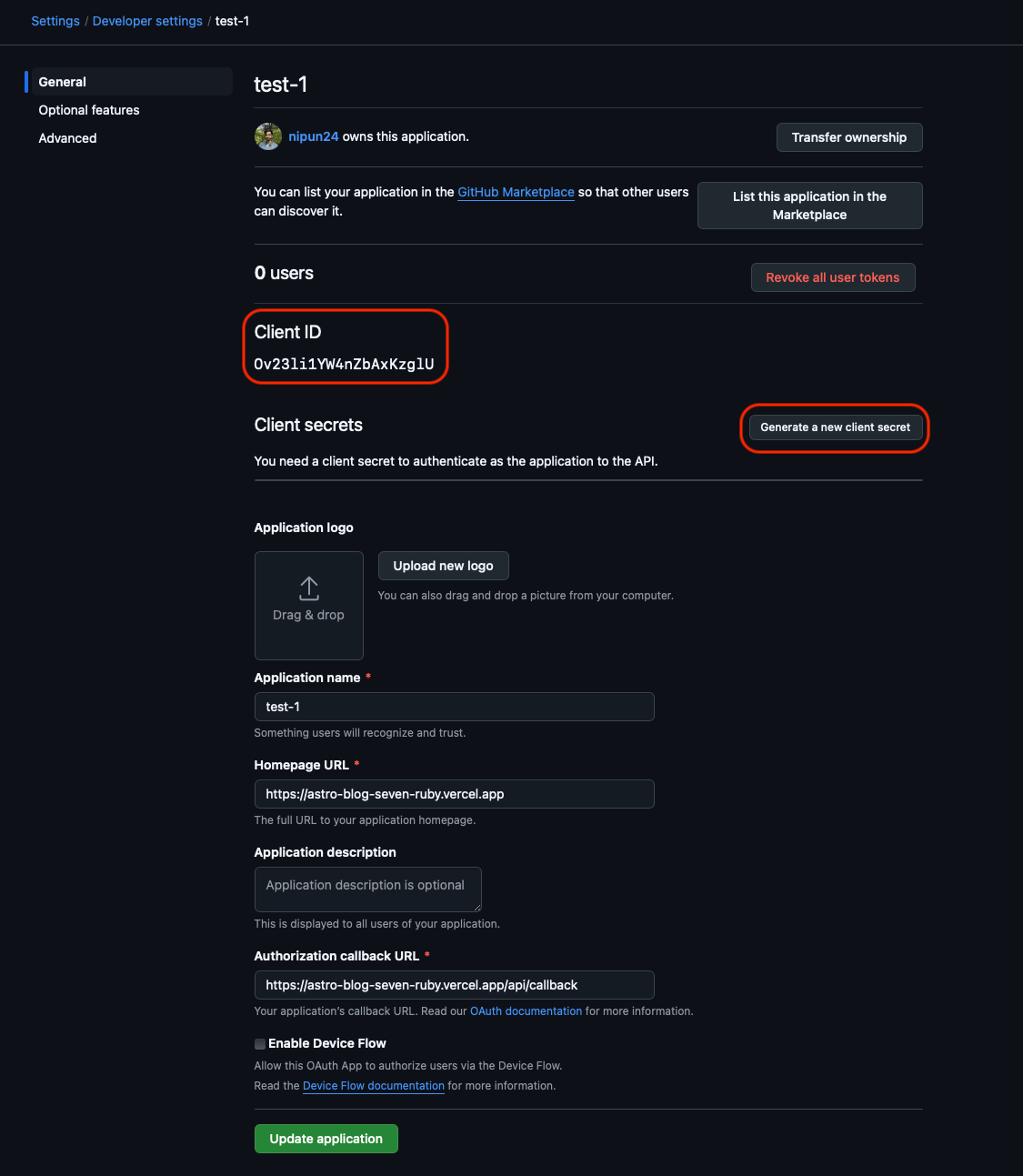
Click Register. On the next page copy the Client ID and Client secret. We’ll need it later.
Adding environment variables in vercel#
In your vercel project go to Settings > Environment variables.
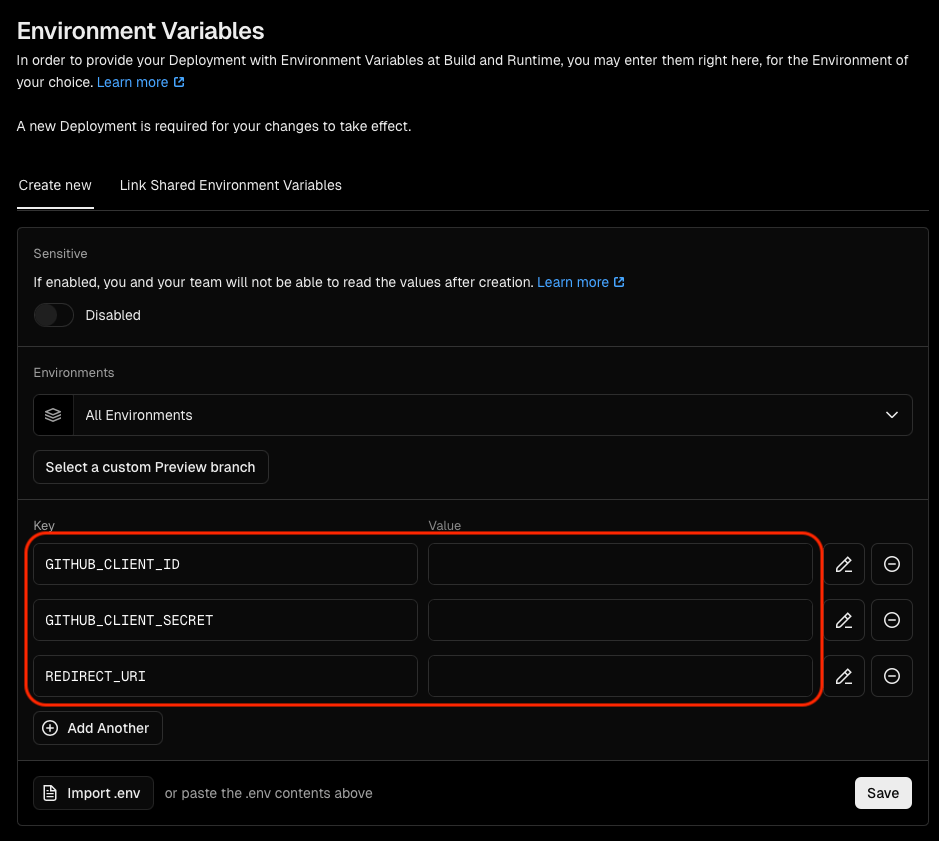
Enter the following values:
- GITHUB_CLIENT_ID: copied from github.
- GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET: copied from github.
- REDIRECT_URI: The url you used in github authorization callback url.
Click Save.
Adding API routes in application#
We’ll use vercel functions to create an API to forward these requests to Github.
Create a directory named api in the root blog directory. Create two files auth.js and callback.js.
auth.js
export function GET(request, res) {
const CLIENT_ID = process.env.GITHUB_CLIENT_ID;
const REDIRECT_URI = process.env.REDIRECT_URI;
const authURL = `https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=${CLIENT_ID}&redirect_uri=${REDIRECT_URI}&scope=repo,user`;
return Response.redirect(authURL, 307);
}
callback.js
import axios from "axios";
export async function GET(req) {
const CLIENT_ID = process.env.GITHUB_CLIENT_ID;
const CLIENT_SECRET = process.env.GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET;
const REDIRECT_URI = process.env.REDIRECT_URI;
const url = new URL(req.url);
const params = new URLSearchParams(url.search);
console.log(url, params);
const code = params.get("code");
console.log(code);
if (!code) {
return new Response(
`<script>window.opener.postMessage({ error: "Missing code" }, "*"); window.close();</script>`
);
}
try {
const tokenResponse = await axios.post(
"https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token",
{
client_id: CLIENT_ID,
client_secret: CLIENT_SECRET,
code,
redirect_uri: REDIRECT_URI,
},
{ headers: { Accept: "application/json" } }
);
const accessToken = tokenResponse.data.access_token;
const content = JSON.stringify({ token: accessToken, provider: "github" });
const message = JSON.stringify(`authorization:github:success:${content}`);
return new Response(
`
<html><body><script>
(function() {
function recieveMessage(e) {
console.log("recieveMessage %o", e)
// send message to main window with da app
window.opener.postMessage(
${message},
e.origin
)
}
window.addEventListener("message", recieveMessage, false)
// Start handshare with parent
console.log("Sending message: %o", "github")
window.opener.postMessage("authorizing:github", "*")
})()
</script></body></html>
`,
{ headers: { "Content-Type": "text/html" } }
);
} catch (error) {
const content = JSON.stringify(error);
const message = JSON.stringify(`authorization:github:error:${content}`);
return new Response(`
<html><body><script>
(function() {
function recieveMessage(e) {
console.log("recieveMessage %o", e)
// send message to main window with da app
window.opener.postMessage(
${message},
e.origin
)
}
window.addEventListener("message", recieveMessage, false)
// Start handshare with parent
console.log("Sending message: %o", "github")
window.opener.postMessage("authorizing:github", "*")
})()
</script></body></html>
`);
}
}
The directory structure will look like this:
📦blog
┣ 📂api
┃ ┣ 📜auth.js
┃ ┗ 📜callback.js
Add production and development config#
Make a copy of the public/admin/config.yml as config.dev.yml and config.prod.yml.
config.dev.yml
collections:
- name: "blog" # Used in routes, e.g., /admin/collections/blog
label: "Blog" # Used in the UI
folder: "src/content/blog" # The path to the folder where the documents are stored
create: true # Allow users to create new documents in this collection
fields: # The fields for each document, usually in frontmatter
- { label: "Title", name: "title", widget: "string" }
- { label: "Description", name: "description", widget: "string" }
- { label: "Publist date", name: "pubDate", widget: "datetime" }
- { label: "Hero image", name: "heroImage", widget: "string" }
media_folder: "src/assets/images" # Location where files will be stored in the repo
public_folder: "src/assets/images" # The src attribute for uploaded media
backend:
name: github
repo: <owner-name>/<repo-name>
branch: main
config.prod.yml
collections:
- name: "blog" # Used in routes, e.g., /admin/collections/blog
label: "Blog" # Used in the UI
folder: "src/content/blog" # The path to the folder where the documents are stored
create: true # Allow users to create new documents in this collection
fields: # The fields for each document, usually in frontmatter
- { label: "Title", name: "title", widget: "string" }
- { label: "Description", name: "description", widget: "string" }
- { label: "Publist date", name: "pubDate", widget: "datetime" }
- { label: "Hero image", name: "heroImage", widget: "string" }
media_folder: "src/assets/images" # Location where files will be stored in the repo
public_folder: "src/assets/images" # The src attribute for uploaded media
backend:
name: github
repo: <owner-name>/<repo-name>
branch: main
base_url: <astro public url>
auth_endpoint: api/auth
Edit the scripts in package.json as follows:
"scripts": {
...
"build": "cp public/admin/config.prod.yml public/admin/config.yml && astro build",
"develop": "cp public/admin/config.dev.yml public/admin/config.yml && vercel dev",
...
},
Now install the following packages
npm i -g vercel
npm i next@latest axios
Check that everything is working locally. You’ll asked to login to vercel. Follow the steps to link the existing project on vercel to your local project.
npm run develop
If everything worked you’ll still be able to open http://localhost:4321/admin/index.html.
Finally deploying everything#
Now we’ll finally commit and push everything again. Wait for the deployment to finish on vercel. Then navigate to
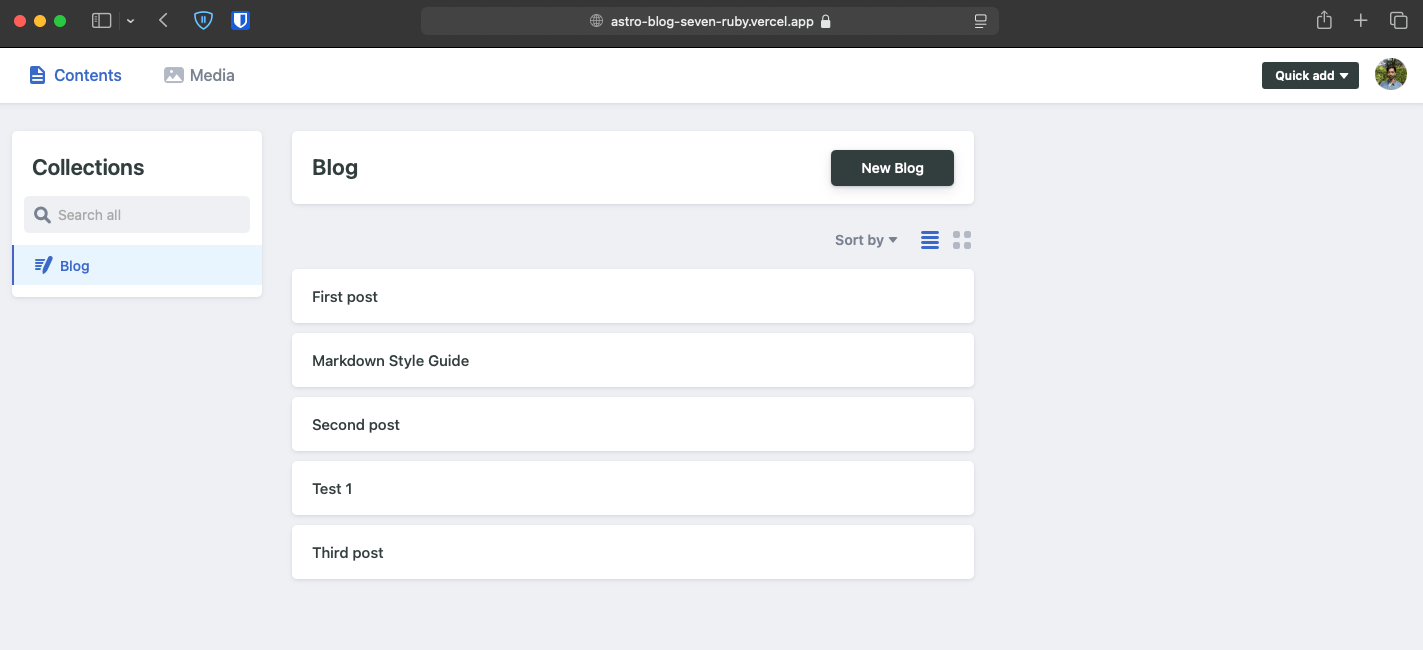
Try to edit a post and publish. The changes will reflected on the site after the build is completed in vercel.
This blog is a bit long. Thank you for making it till the end.🙏
Share with others who might find this useful too.